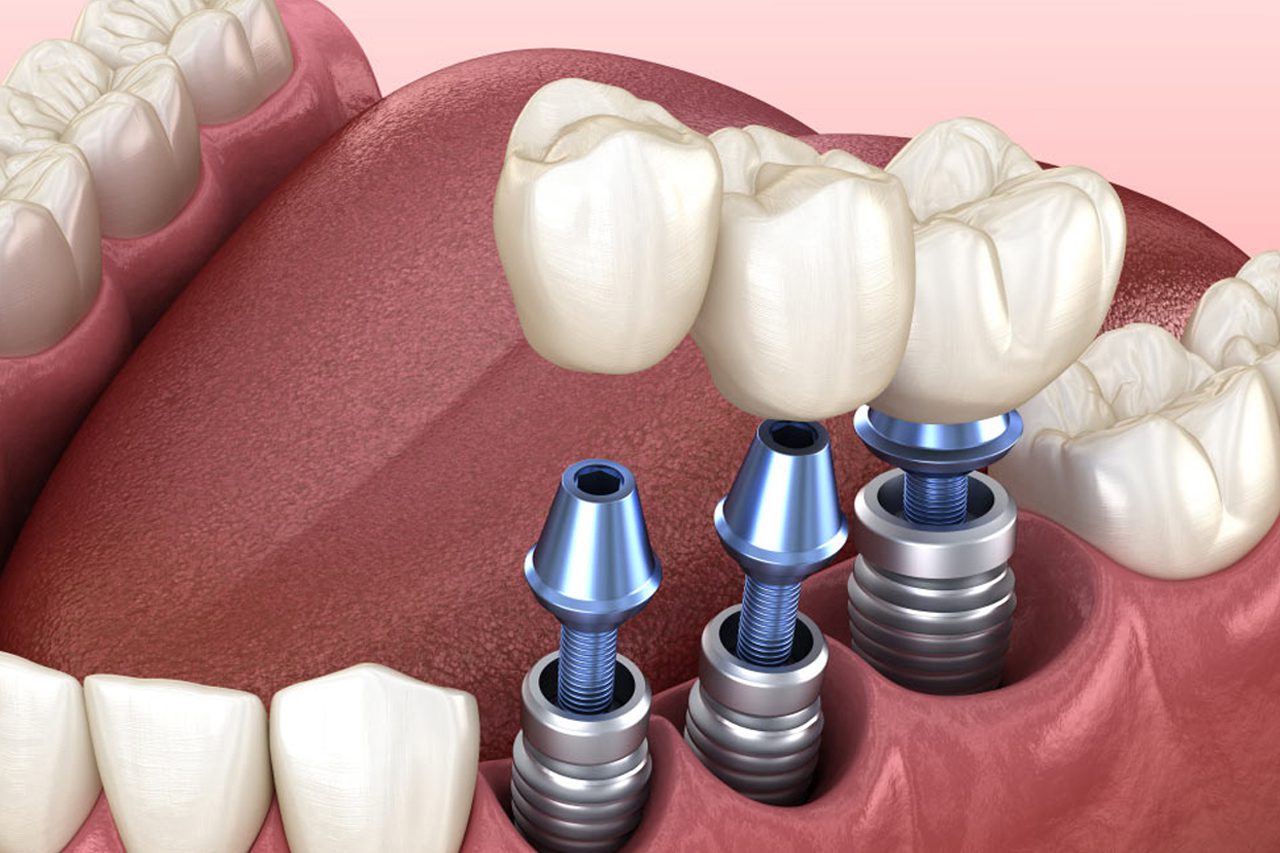
Dental implants have revolutionized the field of restorative dentistry, offering a reliable solution for replacing missing teeth. They are designed to mimic the natural tooth structure and provide a strong foundation for replacement teeth that look, feel, and function like natural teeth. Among the various types of dental implants Sydney, several have demonstrated particularly good success rates. Let’s explore three notable types: Endosteal Implants, Subperiosteal Implants, and Zygomatic Implants.
1. Endosteal Implants
Endosteal implants are the most commonly used type of dental implants due to their high success rates and versatility. These implants are surgically placed directly into the jawbone, where they integrate with the bone tissue through a process called osseointegration. This integration provides a stable anchor for artificial teeth such as crowns, bridges, or dentures.
Key Features:
- Surgical Procedure: Typically performed in stages, starting with the implant placement into the jawbone.
- Material: Often made of titanium, known for its biocompatibility and ability to fuse with bone tissue.
- Versatility: Suitable for most patients with sufficient bone density and volume.
Success Rate: Endosteal implants have shown success rates of up to 95% over ten years when placed by experienced dental professionals and with proper post-operative care.
2. Subperiosteal Implants
Subperiosteal implants are an alternative for patients who have insufficient natural bone height in the jaw for traditional endosteal implants. Instead of being placed into the jawbone, these implants are positioned under the gum but above or on the jawbone. They rest on a metal framework that protrudes through the gum to hold the replacement tooth or teeth securely in place.
Key Features:
- Custom Fit: The metal framework is tailored to fit the contours of the jawbone beneath the gum tissue.
- Procedure: Involves a surgical procedure to place the implant framework beneath the gumline.
- Indications: Suitable for patients with minimal bone height who may not be candidates for traditional implants.
Success Rate: Subperiosteal implants have shown good success rates, particularly in patients with reduced bone density or volume in the jawbone.
3. Zygomatic Implants
Zygomatic implants, also known as zygomaticus implants, are designed for patients who have experienced severe bone loss in the upper jaw and are not candidates for traditional implants due to insufficient bone volume. These implants are longer than standard dental implants and are anchored into the zygomatic bone (cheekbone) rather than the maxillary bone.
Key Features:
- Location: Surgically anchored into the zygomatic bone, providing stability and support.
- Length: Longer than traditional implants to reach the zygomatic bone.
- Complexity: Requires specialized training and expertise in placing implants in the zygomatic bone.
Success Rate: Zygomatic implants have shown favorable success rates, offering a viable option for patients with significant bone loss in the upper jaw.
Understanding the Dental Implant Process:
There are several stages to the dental implant procedure, which makes it more accessible and manageable for patients. Here’s a breakdown of the stages:
- Initial Consultation: Your dentist will assess your suitability for dental implants near me and conduct X-rays to evaluate your jawbone health.
- Preparatory Procedures: This may include bone grafting, tooth extraction, or treatment for gum disease to prepare the jawbone for implant placement.
- Implant Surgery: The implant is surgically placed into the jawbone.
- Placement of Abutments: Once the implant integrates with the bone, abutments are attached to support the final restoration.
- Final Restoration: Custom-designed crowns, bridges, or dentures are placed to restore function and aesthetics.
Conclusion
Choosing the right type of dental implant depends on various factors, including the patient’s jawbone structure, oral health, and overall dental needs. Endosteal implants remain the gold standard due to their widespread use and high success rates. Subperiosteal implants offer an alternative for patients with limited bone volume, while zygomatic implants provide a solution for complex cases of bone loss in the upper jaw.
Consulting with a qualified dental professional is crucial to determine the most suitable type of implant based on individual circumstances. They will also explain the dental implants cost for you. With advancements in implant technology and techniques, dental implants continue to offer patients a durable and natural-looking solution for restoring their smiles.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What are dental implants?
Dental implants are artificial tooth roots made of biocompatible materials like titanium, surgically placed into the jawbone to support replacement teeth such as crowns, bridges, or dentures. They offer a stable foundation for prosthetic teeth that look and function like natural teeth.
2. Who is a suitable candidate for dental implants?
Ideal candidates for tooth implants are individuals with good oral health, sufficient jawbone density, and overall good health. Your dentist will evaluate your oral condition, medical history, and bone structure to determine if you qualify for implants.
3. What are the different types of dental implants?
There are several types of dental implants:
- Endosteal implants: Placed directly into the jawbone.
- Subperiosteal implants: Rest on a metal framework on or above the jawbone.
- Zygomatic implants: Anchor into the cheekbone for patients with severe jawbone loss.
4. How long do dental implants last?
With proper care and maintenance, dental implants can last a lifetime. They have high success rates, often exceeding 95% over ten years when placed by experienced professionals and with good oral hygiene practices.
5. What is the process of getting dental implants? The process typically involves:
- Initial consultation and assessment.
- X-rays to evaluate jawbone health.
- Implant placement surgery.
- Healing period for osseointegration.
- Placement of abutments and final restoration.
6. Are dental implants painful? During the procedure, local anesthesia is used to ensure patients are comfortable. Post-surgery discomfort can be managed with pain medications prescribed by your dentist. Most patients report minimal pain during recovery.
7. How much do dental implants cost? The cost of dental implants varies based on factors like the number of implants needed, type of restoration, and any additional procedures required (such as bone grafting). Financing options are often available to make implants more affordable.
8. What are the benefits of dental implants compared to other tooth replacement options? Dental implants offer several advantages, including:
- Improved aesthetics and natural appearance.
- Enhanced chewing and speaking ability.
- Long-term durability and stability.
- Preservation of adjacent teeth and jawbone structure.
9. Is there a risk of complications with dental implants? While rare, complications can include infection, implant failure (usually due to poor osseointegration), nerve damage, or sinus issues (with upper jaw implants). These risks are minimized with careful planning and skilled surgical techniques.
10. How do I care for dental implants after the procedure? Proper oral hygiene is crucial for the long-term success of dental implants. Brushing, flossing, and regular dental check-ups are essential. Avoiding tobacco use and maintaining a healthy diet also contribute to implant longevity.